The Emerging Disruption of Precision Gene Editing in Healthcare and Beyond
Precision gene editing is advancing beyond traditional CRISPR applications, signaling a potential disruption across healthcare, agriculture, and biotechnology sectors. Recent breakthroughs improving safety, accuracy, and accessibility suggest this emerging trend could reshape disease treatment paradigms, diagnostics, and bioengineering solutions within the next decade. Understanding this weak signal of change is critical for organizations seeking to anticipate shifts in research, regulation, and market opportunities.
What’s Changing?
Gene editing has long held promise for curing genetic diseases by directly modifying DNA sequences. However, persistent challenges around off-target effects and unintended genetic changes have limited its broader adoption. Recent progress documented by MIT scientists reveals new methodologies to substantially enhance accuracy and safety in gene editing. These improvements could accelerate development pipelines for treating hundreds of genetic disorders.
Commercially, companies like CRISPR Therapeutics anticipate significant milestones with products like Casgevy, targeting rare blood diseases. This signals growing market readiness for gene editing solutions beyond laboratory prototypes, moving into regulated clinical use.
Innovations are also extending into diagnostics. Tulane University researchers have developed an enhanced CRISPR-based tuberculosis test using a simple tongue swab (News Medical). This novel approach could democratize infectious disease screening by enabling low-cost, community-based testing, a departure from centralized, lab-dependent diagnostics.
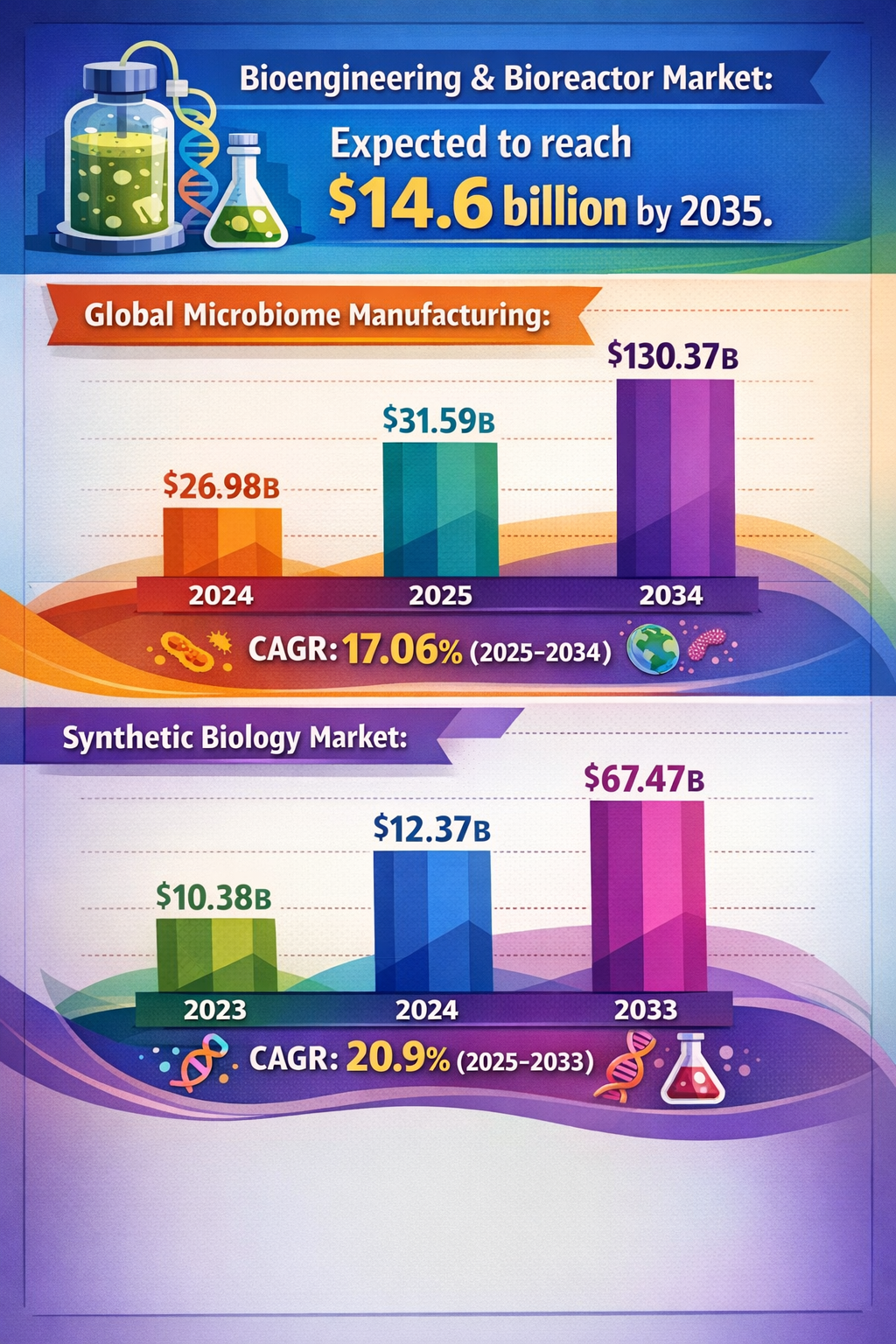
Additionally, the integration of gene editing with artificial intelligence (AI) and systems biology is becoming more prominent. Deep learning models applied to microbiome prediction and nutrient absorption (CNHI News) showcase how AI could optimize bioengineering and precision medicine workflows, amplifying editing outcomes.
From a broader bioeconomy perspective, precision fermentation and cellular agriculture, driven by advances in synthetic biology and gene editing, are poised to redefine food and biotechnology industries (Food Ingredients First). These technologies aim to produce fully functional proteins and alternative food sources, further expanding gene editing’s influence.
Why is this Important?
The convergence of safer, more precise gene editing with scalable diagnostics and AI-driven design introduces a disruptive force with wide-ranging implications. Healthcare stakeholders could face a paradigm shift as curative therapies evolve from symptom management to direct genetic solutions. Diseases once deemed incurable or too complex for gene editing may become treatable, changing patient outcomes and healthcare delivery models.
Diagnostic innovation could enhance early detection and control of infectious diseases globally, particularly in underserved regions, improving public health responses and reducing disease burden. The portability and simplicity of CRISPR-based tests may decentralize healthcare diagnostics, creating challenges and opportunities for regulatory bodies and traditional laboratory services.
In agriculture and food industries, gene editing combined with fermentation technologies promises new product categories with customizable nutritional profiles, reduced environmental footprints, and alternative protein sources. This could disrupt livestock farming economies and supply chains, forcing industry-wide adaptation.
Implications
Organizations across sectors should prepare for an accelerating shift toward precision bioengineering by monitoring regulatory developments, investing in interdisciplinary research, and fostering collaborations between AI, gene editing, and synthetic biology domains. Key implications include:
- Regulatory Complexity: As more gene-edited products enter the market—therapeutics, diagnostics, food—governments may need to update and harmonize regulatory frameworks to address novel risks and ethical considerations.
- Intellectual Property and Access: The balance between incentivizing innovation and ensuring equitable global access to gene-editing technologies will become a critical policy issue.
- Industry Disruption: Traditional pharmaceutical, agricultural, and diagnostic companies might face competition from startups leveraging advanced gene editing and AI, prompting strategic pivots.
- Workforce Evolution: Expertise in genomics, bioinformatics, machine learning, and regulatory science will be increasingly valuable, necessitating workforce training and upskilling.
- Public Perception and Ethical Debate: Transparency and engagement around ethical issues related to gene editing use, particularly for germline editing and food systems, will influence public acceptance and market adoption.
Failure to proactively address these implications could result in missed opportunities or unintended risks, from regulatory bottlenecks to societal backlash.
Questions
- How can organizations integrate emerging precision gene editing technologies into existing R&D pipelines, balancing innovation with compliance risks?
- What strategies can regulators adopt to ensure safety and efficacy without stifling innovation in gene editing applications?
- How might AI-driven predictive models reshape decision-making in bioengineering and clinical gene editing interventions?
- In what ways can cross-sector partnerships accelerate scalable and equitable deployment of gene editing solutions globally?
- What contingency plans should industries develop to address disruptive shifts in supply chains resulting from cellular agriculture and synthetic biology breakthroughs?
Keywords
Precision Gene Editing; CRISPR; Gene Editing Diagnostics; Artificial Intelligence in Biotech; Synthetic Biology; Cellular Agriculture; Precision Fermentation
Bibliography
- In 2026, CRISPR Therapeutics expects significant commercial progress for its lone approved product, Casgevy, which treats two rare blood diseases. Nasdaq. https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/these-2-healthcare-stocks-beat-market-2025-should-you-buy-them-2026
- MIT scientists have found a way to make gene editing far safer and more accurate - a breakthrough that could reshape how we treat hundreds of genetic diseases. Science Daily. https://www.sciencedaily.com/news/top/health/
- Tulane University researchers have developed an enhanced CRISPR-based tuberculosis test that works with a simple tongue swab, a potential breakthrough that could allow easier, community-based screenings for the world's deadliest infectious disease. News Medical. https://www.news-medical.net/medical/news
- Deep Learning, the fastest-growing subsegment, is projected to surpass USD 750 million by 2032 due to adoption in microbiome prediction and nutrient absorption modeling. CNHI News. https://www.cnhinews.com/news/article_a7005ebe-bdad-5fd1-82c6-493564a82740.html
- Sternchemie's Rabeler expects precision fermentation, cellular agriculture, and fully functional proteins to transform the F & B sector in the next five to ten years. Food Ingredients First. https://www.foodingredientsfirst.com/news/protein-innovation-taste-cost.html